NEW QUESTION 153
Sales promotions can involve selling a product at a relatively low price or selling the product with a free (or seemingly free) unit of the product, as in “buy one, get one free” campaigns. Research shows that immediately following month-long sales promotions, a postpromotion dip may occur, i.e., sales for the following calendar month may be less than sales for the calendar month preceding the sales promotion.
To increase sales, Storex, a department store, held month-long sales campaigns to promote four of its products. A sales promotion was considered successful if unit sales of the product were at least 10% higher in each of the 2 calendar months immediately following the promotion than In the month preceding it.
Experts have offered explanations for postpromotion dip:
* Explanation I: Many consumers stockpile the product at relatively low cost during the sales promotion.
* Explanation II: “Buy one, get one free” promotions cause some consumers to undervalue the product, making them less likely to buy it following the sales promotion.
* Explanation HI: Many consumers who missed a “buy one, get one free” opportunity may, as a result, develop so-called inaction inertia, i.e., become less likely to buy the product at either the regular or even at a discount price than if the sales promotion had not occurred.
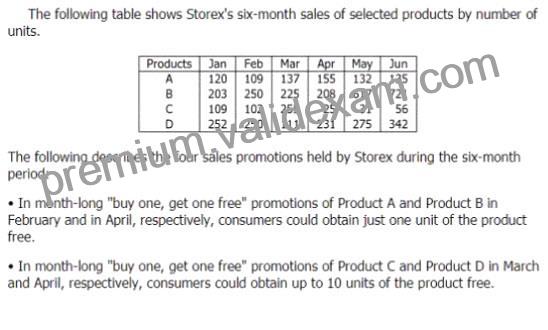
Which one of the following is most strongly supported by the sales data, given the other Information provided?


Leave a Reply